Master Data
Master Data represents the business
objects that are shared across more than one transactional application. This
data represents the business objects around which the transactions are
executed. This data also represents the key dimensions around which analytics
are done. Master data creates a single version of the truth about these objects
across the operational IT landscape.
An MDM solution should to be able to
manage all master data objects. These usually include Customer, Supplier, Site,
Account, Asset, and Product. But other objects such as Invoices, Campaigns, or
Service Requests can also cross applications and need consolidation, standardization,
cleansing, and distribution. Different industries will have additional objects
that are critical to the smooth functioning of the business.
It is also important to note that
since MDM supports transactional applications, it must support highvolume
transaction rates. Therefore, Master Data must reside in data models designed
for OLTP environments. Operational Data Stores (ODS) do not fulfill this key
architectural requirement.
Maximum business value comes from
managing both transactional and analytical master data. Thesesolutions are
called Enterprise MDM. Operational data cleansing improves the operational
efficienciesof the applications themselves and the business process that use these
applications. The resultantdimensions for analytical analysis are true
representations of how the business is actually running.What’s more, the
insights realized through analytical processes are made available to the
operationalside of the business.
Oracle provides the most
comprehensive Enterprise MDM solution on the market today. Oracle MDM spans
analytical, financial, and transactional MDM with its variety of hubs for
customer, product, site, supplier and operational data.
Master Data Management Processes
Now that we have identified the nature of
master data and its place in the information architecture, we need to identify
the key processes that MDM solutions must support.
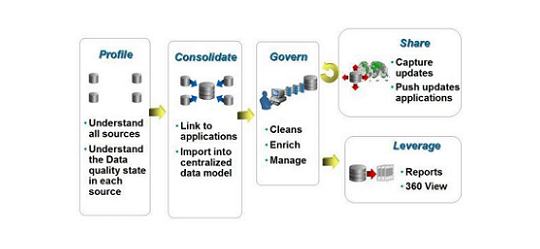
These are the key processes for any MDM system.
- Profile the master data. Understand all possible sources and the current state of data quality in each source.
- Consolidate the master data into a central repository and link it to all participating applications.
- Govern the master data. Clean it up, reduplicate it, and enrich it with information from 3rd party systems. Manage it according to business rules.
- Synchronize the central master data with enterprise business processes and the connected applications. Insure that data stays in sync across the IT landscape.
- Leverage the fact that a single version of the truth exists for all master data objects by supporting business intelligence systems and reporting